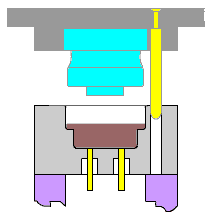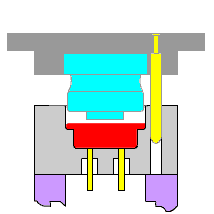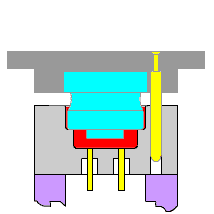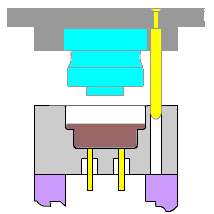
1. Injection
It is a way to produce industrial products. Products generally use rubber injection molding and plastic injection molding. Injection molding can also be divided into injection molding compression method and die-casting method. Injection molding machine (abbreviated as injection molding machine or injection molding machine) is the primary molding equipment that uses plastic molding molds to make various shapes of plastic products from thermoplastics or thermosets. Injection molding is achieved through injection molding machines and molds.
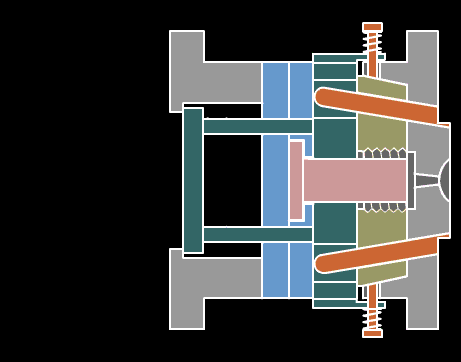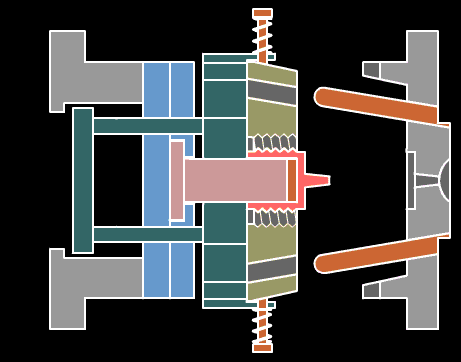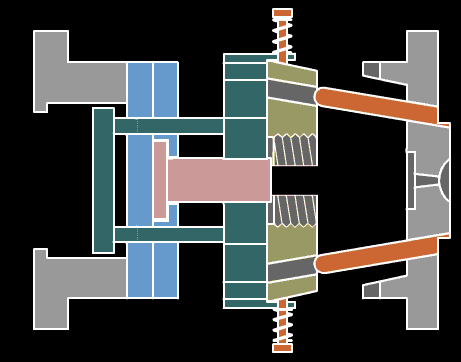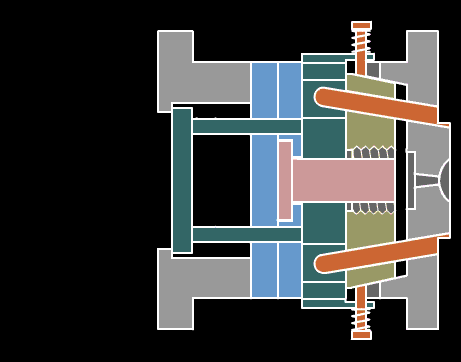
2. Extrusion
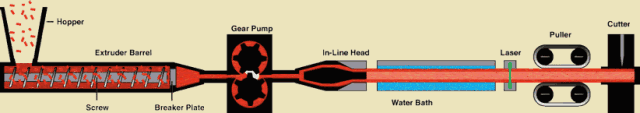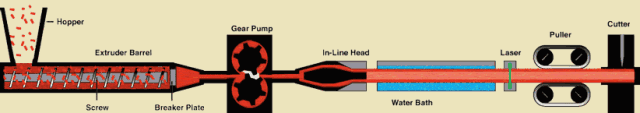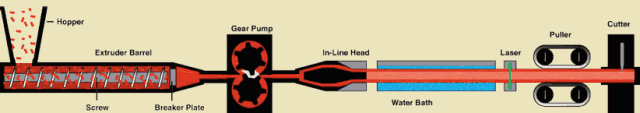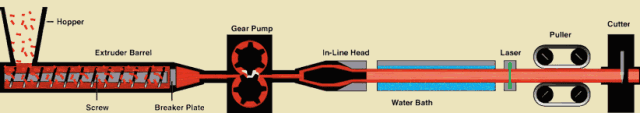
The material passes through the action between the barrel of the extruder and the screw, while being plasticized by heat, is pushed forward by the screw, and then passes through the head to make various cross-section products or semi-products.
3. Rotational molding
Also known as rotational molding, rotational molding, rotational molding, rotational casting, rotational molding, etc., the molding method is to first put the measured plastic (liquid or powder) into the participating mold, and after the mold is closed, make it along the two sides The straight rotating shaft rotates and the mold is heated at the same time. Under the action of gravity and thermal energy, the plastic material in the mold is gradually uniformly coated, melted and adhered to the entire surface of the mold cavity, and formed into the same shape as the mold cavity. After cooling, shaping and demolding, products of the desired shape are obtained.

4. Blow molding
Also known as hollow blow molding, it is a rapid plastic processing method. The tubular plastic parison obtained by extrusion or injection molding of the thermoplastic resin is placed in a split mold while it is hot (or heated to a softened condition). After the mold is closed, compressed air is injected into the parison to blow the plastic parison. It expands and clings to the inner wall of the mold, and after cooling and demolding, various hollow products are obtained.
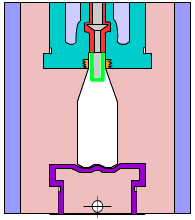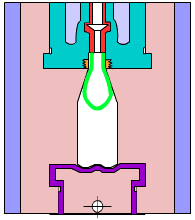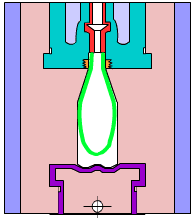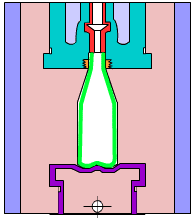
5. Blister
A plastic processing technology. The primary principle is to heat a flat plastic hard sheet to soften it, then select a vacuum to absorb it on the surface of the mold, cool it and form it, and apply it to all walks of life.

6. Compression molding
Also known as restricted molding or compression molding, it is the operation of first putting powdered, granular or fibrous plastic into the mold cavity at the molding temperature, and then closing the mold to press to shape and solidify it. Compression molding can be used for both Thermosetting plastics, thermoplastics and rubber materials.
7. Calendering
The melted and plasticized thermoplastic is passed through two or more parallel and counter-rotating roller gaps, so that the melt is kneaded, stretched and stretched by the rollers to become a continuous sheet product with certain specifications and dimensions and quality requirements. The method of forming by natural cooling. The calendering process is often used in the production of plastic films or sheets
.

8. Foam molding
It is the process of adding proper foaming agent to the foaming materials (PVC, PE, PS, etc.) to make the plastic have a microporous structure. Almost all thermosetting and thermoplastic plastics can be made into foam, and foam molding has become an important category in plastic processing.
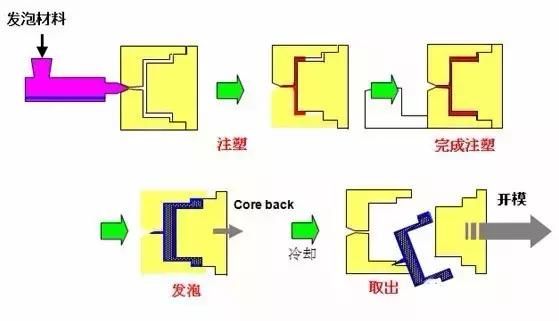
Flow chart of micro-foaming skills
Flow chart of micro-foaming skills
9. Surround molding
The process is to wrap the continuous fiber (or cloth tape, prepreg yarn) impregnated with resin glue on the core mold according to a certain rule, and then solidify and demold to obtain the product.
10. Laminate molding
It refers to a forming method that combines multiple layers of the same or different materials as a whole under heating and pressure. Commonly used in plastic processing, but also in rubber processing.
11. Coating and molding
It is a process of using plastisol or organosol to coat the surface of substrates such as cloth or paper to make imitation leather products, varnished cloth or plastic wallpaper, or to coat powdered plastic with metal surfaces. Common plastic coated products include artificial leather, varnished cloth, plastic wallpaper and various metal coated products.
12. Pouring molding
It is a method of plastic processing. In the early casting, liquid monomers or prepolymers were injected into the mold under normal pressure, and after polymerization, it was solidified and formed into a product with the same shape as the cavity of the mold. The emergence of nylon monomer casting in the 1960s saw the development of polyamide following the development of molding skills. The traditional casting concept has changed. Polymer solutions and dispersions refer to PVC pastes and melts that can also be used for casting.
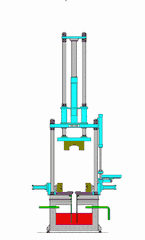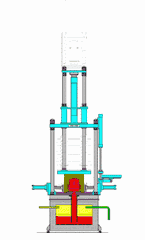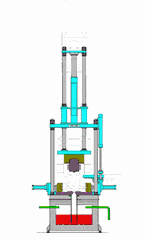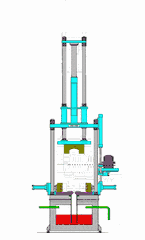
13.Dipsu
The skill is to use thermoplastic polymer materials to have variable conditions, that is, to have viscous flow under certain conditions, and to restore the solid state at room temperature, and to use appropriate methods and special tools to ink jets in their viscous flow. Under the condition, it is molded into the planned shape as required, and then cured and molded at room temperature.

14. Cold press molding
It is a kind of compression molding. Different from general compression molding, the material is pressure-molded at room temperature. After demolding, the molded product can be reheated or cured by chemical action.
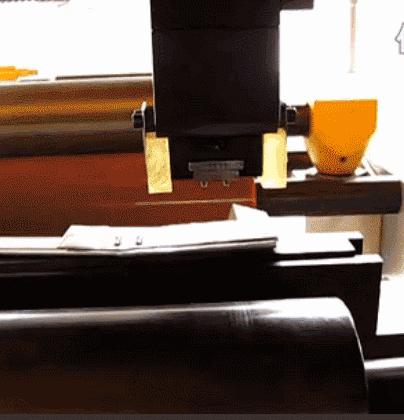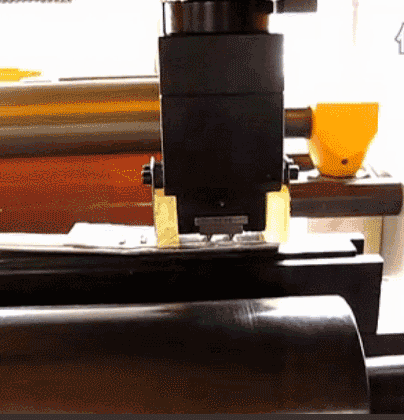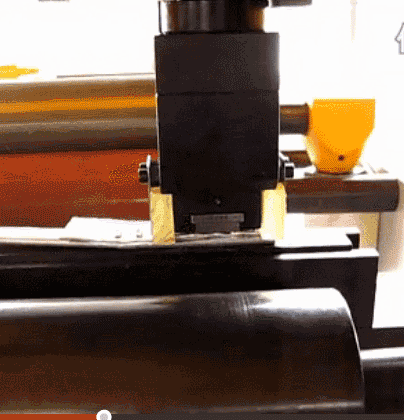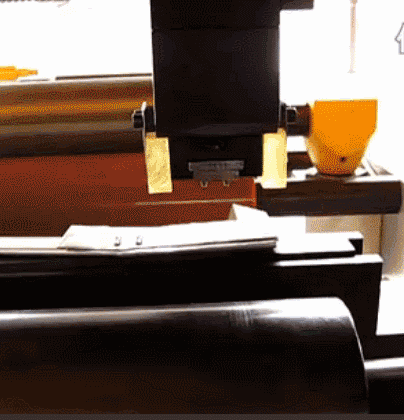
15. Compression molding method
It is mainly used for the production of thermosetting plastic products. The molding is heated to melt, press the die, and then cross-link and solidify through heating, and the product is obtained after demolding.
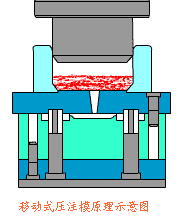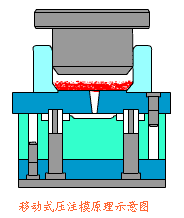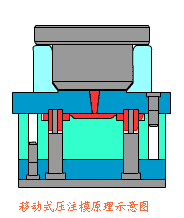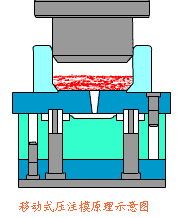
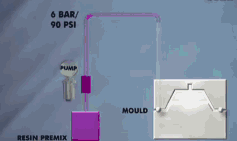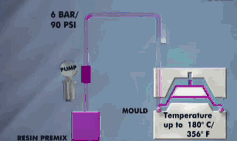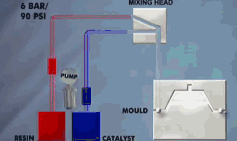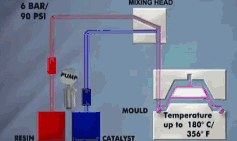
16. Resin transfer molding
It is a process of injecting resin into a closed mold to moisturize and strengthen the material and solidify it. This skill eliminates the need for prepregs and autoclaves, effectively reducing equipment costs and molding costs. This skill has been developed rapidly in recent years and has been widely used in the aircraft industry, automobile industry, and shipbuilding industry. Various branches such as RFI, VARTM, SCRIMP, SPRINT, etc. have been discussed and developed to meet the application needs of different fields.
17. Kneading
It is a pressure processing method in which a punch or a punch is used to pressurize the blank placed in a concave mold to cause it to undergo plastic flow, and then obtain a part corresponding to the shape of the mold hole or concave and convex mold. During kneading, the billet generates three-dimensional compressive stress, and even the billet with low plasticity can be kneaded into shape.
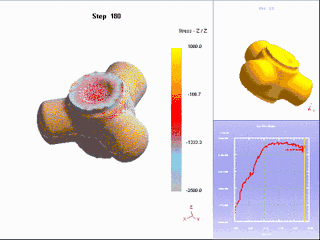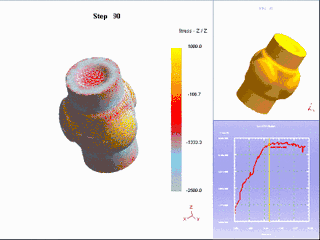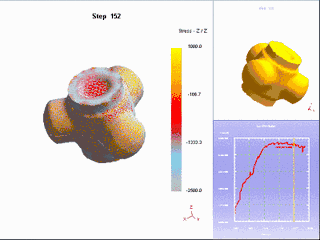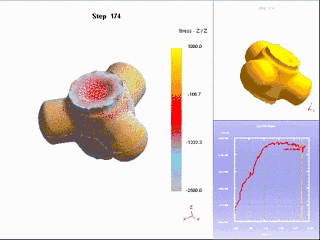
18. Thermoforming
It is a special plastic processing method for processing thermoplastic plastic sheets into various products. A special plastic processing method for processing thermoplastic plastic sheets into various products. The sheet material is clamped on the frame and heated to a softened state, and under the action of external force, it is made to close to the mold surface to obtain a shape similar to the mold surface. After cooling and shaping, the finished product is ready to be finished.
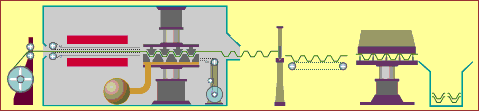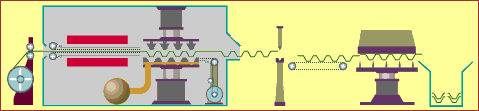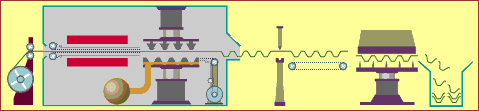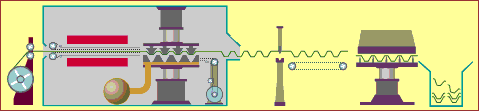
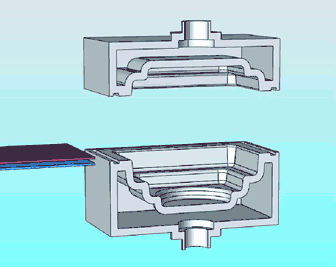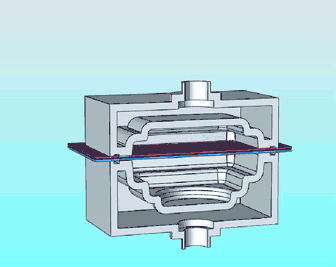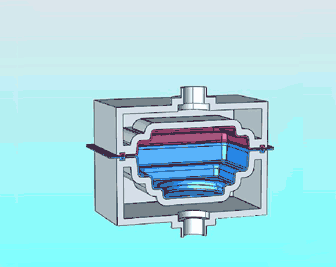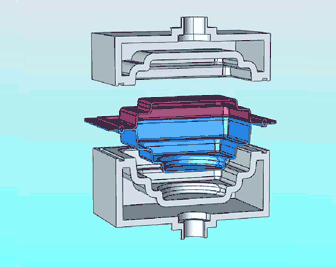
19. 3D printing
(3D) is a kind of rapid prototyping technology, which is based on digital model files, using powdered metal or plastic and other bondable materials to construct objects through a layer-by-layer printing method. 3D printing is generally achieved by using digital skill data printers. It is often used to make models in the fields of mold making, industrial planning, etc., and then gradually used in the direct production of some products. There are already parts printed using this technology.
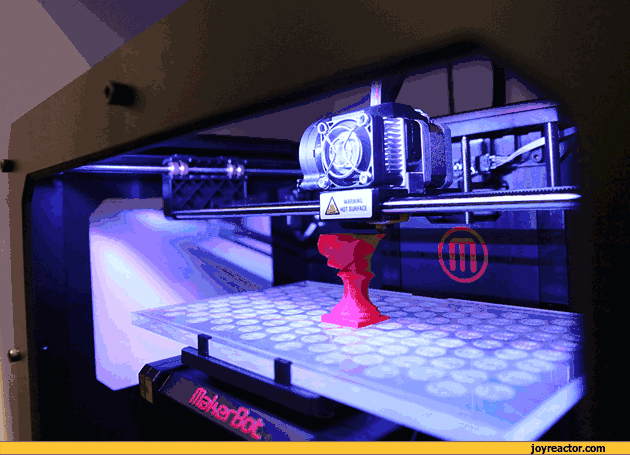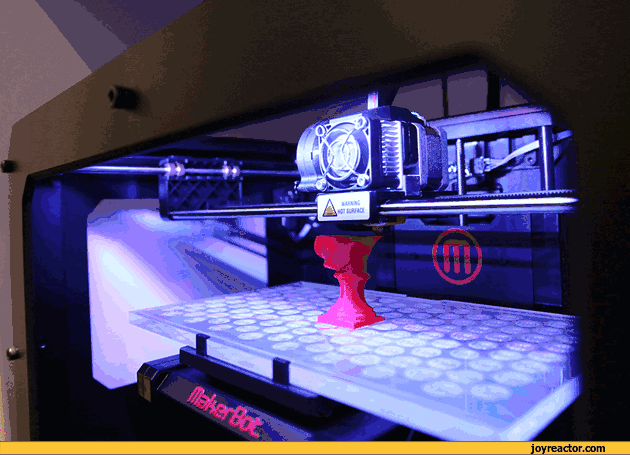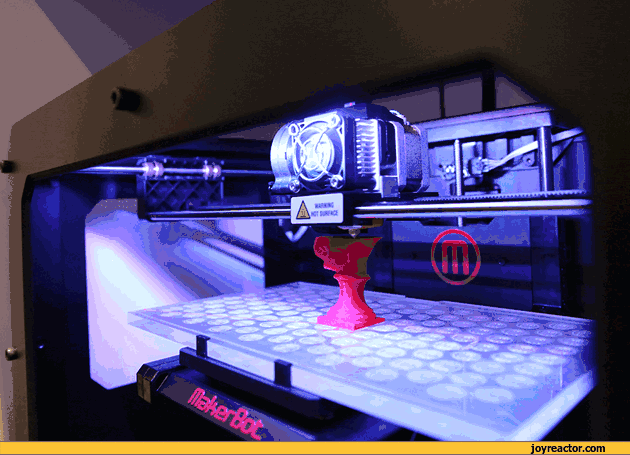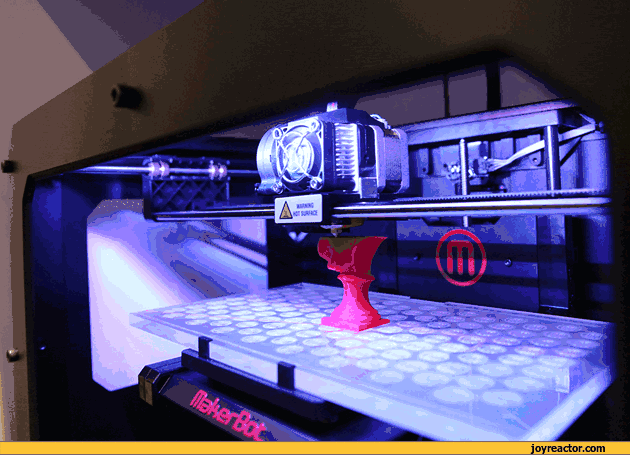
There are many different skills in 3D printing. The difference between them lies in the method of using available materials and building components in different layers. Commonly used materials for 3D printing include nylon glass fiber, polylactic acid, ABS resin, durable nylon materials, gypsum materials, aluminum materials, titanium alloys, stainless steel, silver-plated, gold-plated, and rubber materials.